Exercises
- Fill in the blanks with the proper words:
Click on the question to view the answer
Click on the question to view the answer
400 nm to 800 nm
radio
Subramanian Chandrashekhar
Galileo
Nainital
- Form Pairs:
Click on the question to view the answer
Click on the question to view the answer
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| (i) X-rays | (d) Chandra |
| (ii) Optical Telescope | (c) Hubble |
| (iii) Indian Radio Telescope | (a) GMRT |
| (iv) Launching artificial satellites | (b) ISRO |
- What are the difficulties in using ground based optical telescopes? How are they overcome?
- The visible light coming from a heavenly body has to pass through the earth’s atmosphere to reach the earth’s surface.
- During this journey, some of the light is absorbed by the atmosphere and the intensity of the light reaching the earth’s surface decreases.
- A second problem is caused by the changes in atmospheric pressure and temperature.
- These changes cause turbulence in the atmosphere which in turn cause of the light rays to change their path slightly and thereby shake the position of the image.
- Also, because of Sunlight, we cannot use optical telescopes during the day. During the night too city lights and cloudy weather can cause difficulties in observing the heavenly bodies.
- To reduce these problems, optical telescopes are situated on top of the mountains, at uninhabitated places.
- However, if we want to get rid of all the above problems completely, we should place the telescope above the earth’s atmosphere, in the space itself.
- These problems do not exist in the space and thus the image obtained by space telescopes would be sharp, bright, steady and very clear.
- Which type of telescopes can be made using a concave mirror, convex mirror, plane mirror and a lens? Draw diagrams of these telescopes.
Both Newtonian and Cassegrain types of optical telescopes can be made using these materials.
A line diagram of a Newtonian Reflector Telescope is shown here.
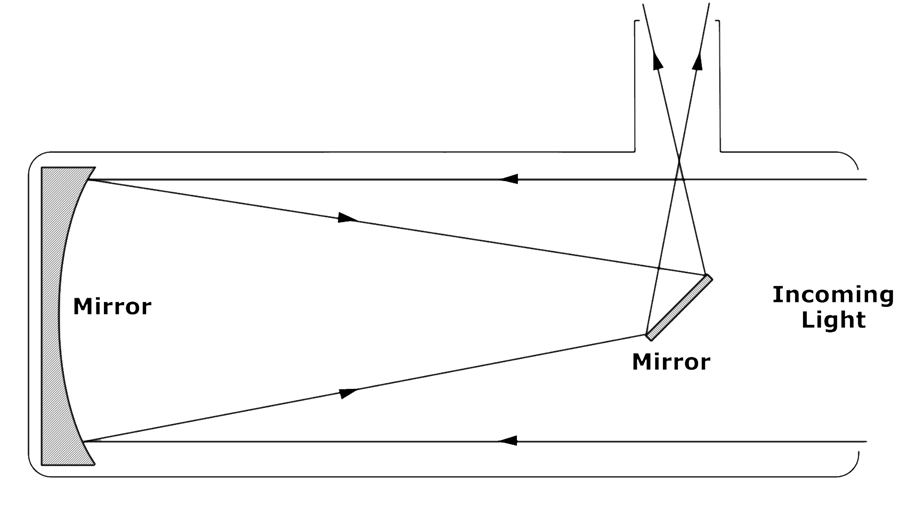
- Study the figure and answer the following questions:
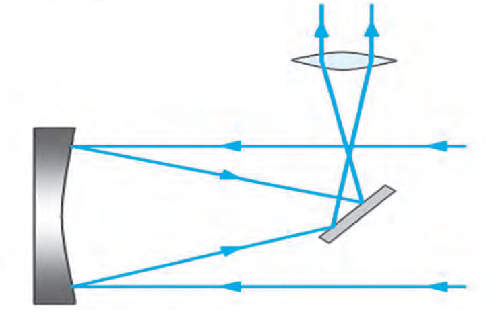
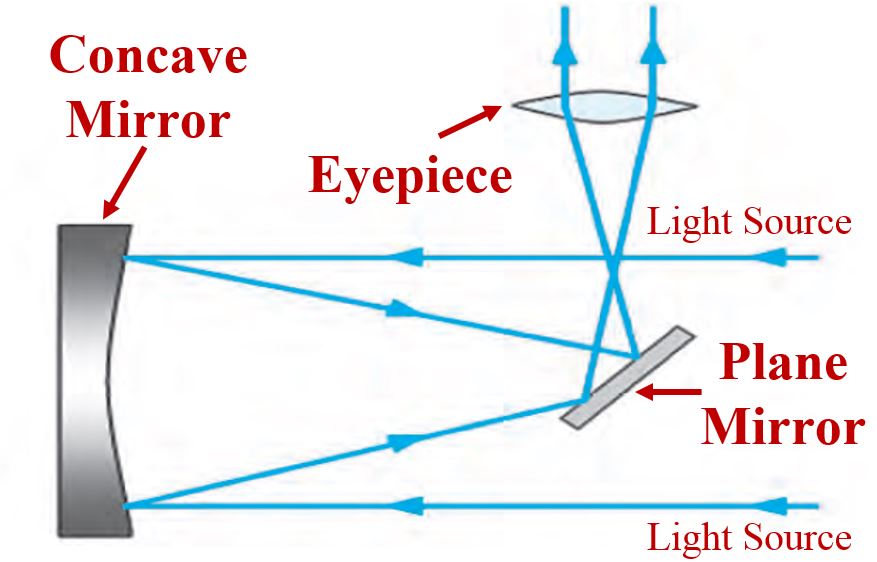
Newtonian Telescope
Concave Mirror
Cassegrain Telescope
- The distance between the concave mirror and the plane mirror can be adjusted.
- The light rays coming from distant objects are parallel to each other.
- These parallel rays are reflected from the concave surface of the mirror.
- A diminished and inverted image is formed in front of the plane mirror.
- This image is again reflected and serves as an object for the eyepiece.
- The eyepiece acts like a simple microscope and a magnified image of the object is obtained.
- Observer can see this image through the eyepiece.
- Answer the following questions:
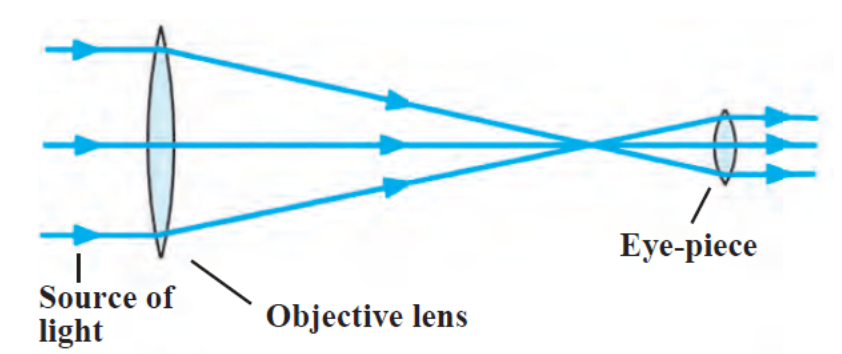
- Galileo’s telescope is a simple refracting telescope.
- It consists of two convex lenses arranged coaxially in a metal tube.
- The distance between the lenses can be changed.
- One of the lens is called the objective while the other is called the eye piece.
- In addition to visible radiation, many heavenly objects emit radio waves. We cannot see this radiation with our eyes.
- Hence, a special type of telescope is used to receive these rays. It is called a radio telescope.
- It is made from one or more dishes of a particular parabolic shape.
- As in optical telescope the incident radio waves are reflected by these dishes and converge at the focus.
- A radio receiver is placed at the focal point.

- The waves and radiation emitted by the heavenly bodies passes through the atmosphere before reaching the earth.
- Some part of this radiation is absorbed by the earth’s atmosphere and it’s intensity decreases.
- In addition to this, temperature, cloud cover, air pressure etc. act as barriers to this radiation.
- Bright sunlight during the day and city lights during the night also put limitations on using the optical telescopes.
- To reduce the intensity of these problems, optical telescopes are placed in uninhabited places on mountains.
- X-rays cannot reach the surface of the earth due to some constraints like atmosphere, temperature, air pressure, cloud cover.
- Hence, X-ray telescope can not be based on the earth.