- Sketch and explain the structure of DNA and various types of RNA.
Structure of DNA:
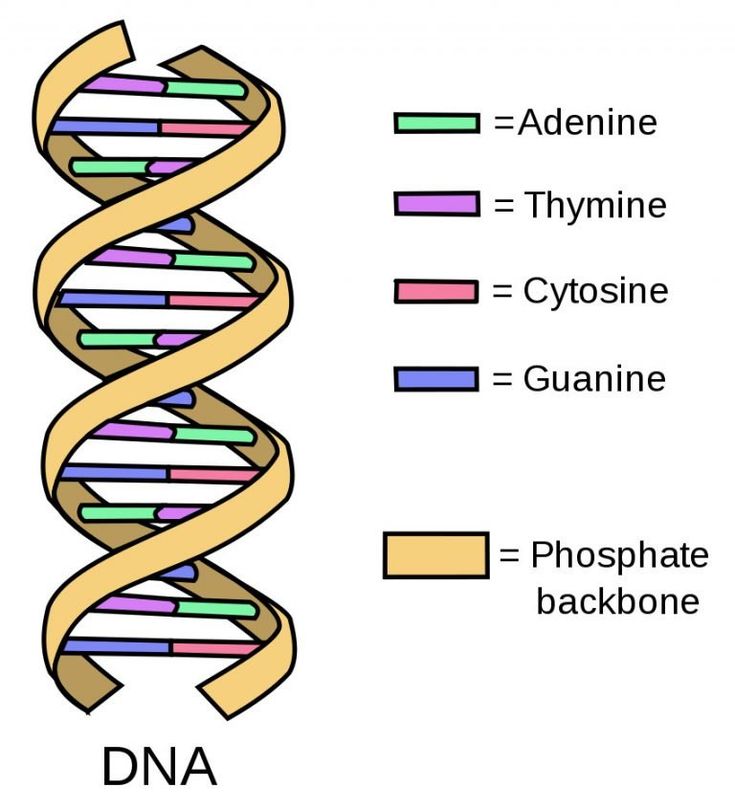
- DNA is made of two linked strands in the shape of a double helix.
- Each strand is made up of nucleotides.
- Each strand has a backbone made of deoxyribose sugar, phosphoric acid and a nitrogenous base.
- Nitrogenous bases are of two types: purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine).
- Adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T) with double hydrogen bond.
- Cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G) with triple hydrogen bond.
Types and functions of RNA:
- Unlike DNA, RNA is a ribonucleic acid having a single strand of ribonucleotides.
- Each ribonucleotide is made up of ribose sugar, phosphate molecules and a nitrogenous base.
- According to their functions, RNAs are of three types: Each strand has a backbone made of deoxyribose sugar, phosphoric acid and a nitrogenous base.
- mRNA: mRNA or messenger RNA carries the information for protein synthesis from genes on DNA chain in nucleus, to ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
- rRNA: rRNA or ribosome RNA helps in protein synthesis.
- tRNA: tRNA or transfer RNA carries the specific amino acid up to the ribosome as per the message coded on mRNA.
- Explain the meaning of genetic disorders and give names of some disorders.
- The disorders caused due to abnormalities in chromosomes and mutations in genes are called genetic disorders.
- Haemophilia, Colour blindness, sickle cell anaemia, Down’s Syndrome, Cleft lip are some examples of genetic disorders.