Answer in detail:
- Explain the glycolysis in detail.
- The process of glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm.
- In this process, a molecule of glucose is oxidized step by step and two molecules of each i.e. pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water are formed.
- Molecules of pyruvic acid formed in this process are converted into molecules of Acetyl-Coenzyme-A.
- Two molecules of NADH2 and two molecules of CO2 are released during this process.
- It is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
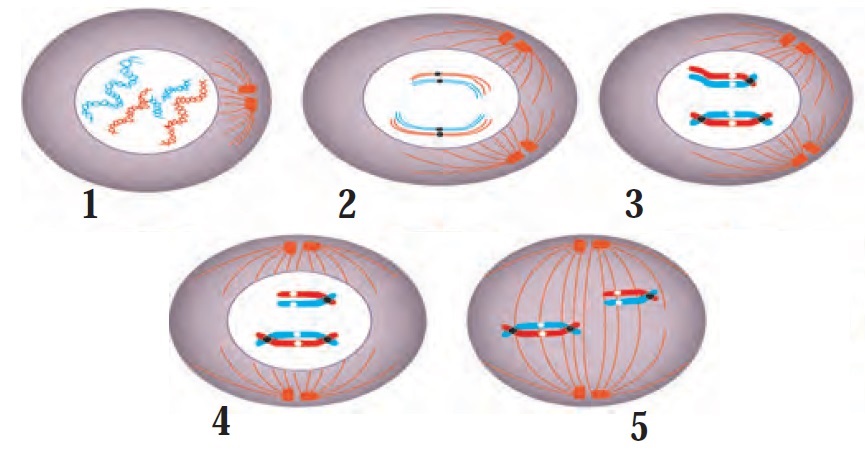
- With the help of suitable diagrams, explain the mitosis in detail.
- Prophase: In prophase, condensation of basically thin thread-like chromosomes starts. Due to this, they become short and thick and they start to appear along with their pairs of sister chromatids. Centrioles duplicate and each centriole moves to opposite poles of the cells. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus start to disappear.
- Metaphase: Nuclear membrane completely disappears in metaphase. Chromosomes complete their condensation and become clearly visible along with their sister chromatids. All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane (central plane) of the cell. Special type of flexible protein fibers (spindle fibers) are formed between centromere of each chromosome and both centrioles.
- Anaphase: In anaphase, centromeres split and thereby sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and they are pulled apart in opposite directions with the help of spindle fibers. Separated sister chromatids are called as daughter chromosomes. Chromosomes being pulled appear like bunch of bananas. In this way, each set of chromosomes reach at two opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase: The chromosomes which have reached at opposite poles of the cell now start to decondense due to which they again become thread-like thin and invisible. Nuclear membrane is formed around each set of chromosomes reached at poles. Thus, two daughter nuclei are formed in a cell. Nucleolus also appears in each daughter nucleus. Spindle fibers completely disappear.
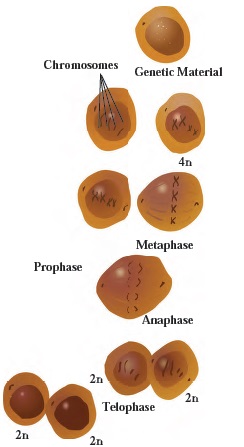
Somatic cells and stem cells divide by mitosis. Mitosis is completed through two main steps. Those two steps are karyokinesis (nuclear division) and cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division). Karyokinesis is completed through four steps:
In this way, karyokinesis completes and cytokinesis begins.
The cytoplasm divides by cytokinesis and two new cells are formed which are called as daughter cells. In this process, a notch is formed at the equatorial plane of the cell which deepens gradually and thereby two new cells are formed. However, in case of plant cells, instead of the notch, a cell plate is formed exactly along midline of the cell and thus cytokinesis is completed.
Mitosis is essential for growth of the body. Besides, it is necessary for restoration of emaciated body, wound healing, formation of blood cells, etc.
- With the help of suitable diagrams, explain the five stages of prophase-I of meiosis.
- Meiosis is completed through two stages.
- Those two stages are meiosis-I and meiosis-II.
- In meiosis-I, recombination / crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes and thereafter those homologous chromosomes (Not sister chromatids) are divided into two groups and thus two haploid cells are formed.
- How all the life processes contribute to the growth and development of the body?
- The Nutrition process supplies the body with essential nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, vitamins essential for growth.
- In the Respiration process the food is oxidized and energy is released. This energy is used to carry out various metabolic activities.
- The excretion process throws out the toxic waste generated in the body during various metabolic activities.
- Oxygen and nutrients are transported by the circulatory system to all the parts of the body.
- The hormones which control the growth are secreted by the endocrine glands. They too are transported by the circulatory system.
- It is through control and coordination that various processes are carried out in harmony.
- Thus, all the life processes contribute to the growth and development of the body.
- Explain the Krebs’ cycle with reaction.
- Both molecules of acetyl-CoA formed by the process of glycolysis enter the mitochondria.
- Cyclic chain of reactions called as tricarboxylic acid cycle is operated on it in the mitochondria.
- Each acetyl-CoA (2C) combines with an oxaloacetic acid (4C) to make a 6C compound (citric acid).
- Acetyl part of acetyl-CoA is completely oxidized through this cyclical process and molecules CO2, H2O, NADH22, FADH2 are derived.